Salmonellosis: symptoms, cause, incubation, how to avoid it?
More than 500,000 batches of eggs have been withdrawn from sale in certain stores (Auchan, Carrefour, Leclerc, etc.) because they are said to be contaminated with salmonella and likely to cause salmonellosis. What are the symptoms of this food poisoning? The incubation period of the bacteria? The treatments to kill it and cure the infection?
[Updated Monday, June 15, 6:02 p.m.] Eating certain foods raw or undercooked can lead to salmonellosis, a foodborne infection that is characterized by gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain and sometimes fever.
Definition: what is salmonella and salmonellosis?
Salmonella (or Salmonella) is a bacterium that causes salmonellosis and typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Salmonella are bacteria that accumulate in the digestive system and can lead, for the most part, to generalized infections, or sepsis. Salmonella is one of the main causes of diarrheal disease worldwide. The number of salmonellosis tends to increase in industrialized countries. It is estimated that 15% of Salmonella are imported into Europe following trips to Africa or Asia. Note that 90% of reptiles, birds and pets carry Salmonella and can transmit it to their owner. As for Salmonella responsible for typhoid and paratyphoid fever, 17 million infections are recorded each year in the world, this time especially in poor countries.
Salmonellosis refers to all infectious diseases caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. Most cases of salmonellosis are mild, but sometimes the disease is life-threatening. The severity of illness depends on host factors and the Salmonella serotype.
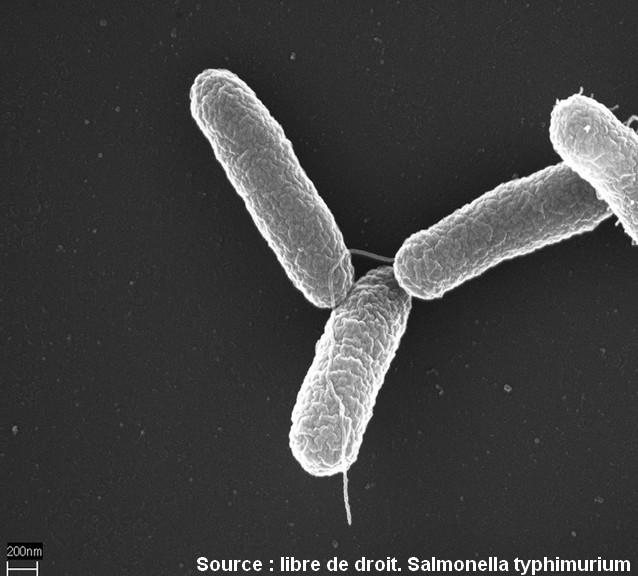
Photo of Salmonella
Types of Salmonella
Salmonella is a genus of gram-negative bacilli belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. Within two species, Salmonella bongori and Salmonella enterica, more than 2500 different serotypes have been identified. They are ubiquitous and resistant bacteria, which can survive for several weeks in a dry environment and several months in water. Among them, Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi are responsible for typhoid fever.
Contagion: how is Salmonella transmitted?
Salmonella are found in most domestic and wild animals. They are present in animals intended for human consumption such as poultry, pigs and cattle, but also in pets, cats, dogs, birds and reptiles, such as turtles. Salmonella can pass through the entire food chain, from animal feed, in primary production and back up the entire chain to households, catering services and institutions. Human beings generally contract salmonellosis by consuming contaminated food of animal origin (mainly eggs, meat, poultry and milk), but also raw vegetables or contaminated vegetables (cucumbers, salads, etc.) or untreated water. Cases also occur in humans through contact with infected animals, especially pets. Often these animals show no signs of illness.
What is the incubation period?
The incubation time is 6-72 hours (usually 12-36 hours) after salmonella ingestion, and the condition lasts 2-7 days.
Symptoms
Salmonellosis is usually characterized by:
Symptoms are generally relatively mild and, in the majority of cases, patients recover without special treatment. In some cases, however, especially in very young children and the elderly, the associated dehydration can become severe and life-threatening.
Cause
Salmonellosis is an infection always caused by the ingestion of salmonella, particularly the consumption of contaminated foods such as eggs, red meats, poultry, seafood...
People at risk
Salmonellosis can affect the entire population. However, it can more seriously affect babies, young children, pregnant women, the elderly, people who have health problems or are immunocompromised.
Diagnostic
To make the diagnosis, the indication of a recent trip to tropical countries or those of North Africa can be evocative. It is advisable to preferably consult the attending physician, an emergency or infectiology service.
The following serology results indicate a recent or old infection:
The presence of type O antibodies, without type H antibodies indicates a recent infection. A high level of O and H antibodies shows an ongoing infection. An isolated elevation of type H antibodies means very old salmonellosis.
Treatment: how to destroy the bacteria and cure the infection?
"In all cases, salmonellosis requires medical advice. A fortiori, typhoid and paratyphoid fevers require rapid medical care," says Dr. Claire Lewandowski, specialist in general medicine. Routine antibiotic therapy is not recommended for mild or moderate forms in otherwise healthy subjects to avoid selecting resistant strains. Only infants, the elderly, pregnant women and immunocompromised patients may need to receive antibiotic therapy. Antimicrobials are also given if the infection spreads from the intestines to other parts of the body. In the most serious cases, a supply of electrolytes (to replace, for example, sodium, potassium and chloride ions, lost following vomiting and diarrhea) and intravenous rehydration are prescribed during hospitalization.
At the same time, the patient must be isolated to avoid transmission and relatives must be screened and treated if necessary. A control of blood cultures is necessary at the end of treatment to ensure healing. In addition, reporting the disease to the Regional Health Agency is mandatory.
• Natural remedies
A decoction of Guava Leaves can be used as a natural remedy in the treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms, to be used only after the agreement of your doctor. The consumption of vegetable activated charcoal, blond psyllium, or probiotics can also be used in case of diarrhea, as can homeopathy: Arsenicum album 15 CH, Phosphorus 15 CH and Veratrum album 7 CH.
• Foods to favor and to avoid
To help restore intestinal transit, it is advisable to avoid consuming milk, green vegetables and fruits, but to favor rice, ham, meat, fish, bananas, apples, quince, or blueberries and drink water and rehydration solutions.
Prevention, cooking: how to avoid infection?
To avoid being affected by salmonella, untreated water and questionable foods should not be consumed, especially in risk areas. The Health Watch Institute checks, in France, the correct conditions for preparing and storing food. To avoid contamination, the WHO advises to:
Thanks to Dr Claire Lewandowski for her medical validation.
Salmonellosis: symptoms, cause, incubation, how to avoid it?DefinitionPhotoTypes of salmonella s ContagionIncubationSymptomsCausePeople at riskDiagnosisTreatments•Natural remedies•Foods to avoid and favorHow to avoid? ...
I manage my push subscriptions